
Monday, July 30, 2012
Synthesis and Property of Temperature-Responsive Hydrogel with Movable Cross-linking Points
Kazuhiro Ishida, Takahiro Uno, Takahito Itoh, and Masataka Kubo
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/ma301065j
The authors prepared a mechanically cross-linked gel using a cyclic PEG macromer co polymerized with NIPAAm. The pNIPAAm chain sections can thread through the PEG cycles, creating movable physical cross-links. Gels were characterized by swelling kinetics and compared to gels made of a linear PEG macromer copolymerized with pNIPAAm using bisacrylamide as a chemical crosslinker. The cycle-containing gels showed significantly higher swelling compared to gels containing the same amount of PEG in linear form. The authors attribute this to the movable nature of the threaded cross-links.
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/ma301065j
The authors prepared a mechanically cross-linked gel using a cyclic PEG macromer co polymerized with NIPAAm. The pNIPAAm chain sections can thread through the PEG cycles, creating movable physical cross-links. Gels were characterized by swelling kinetics and compared to gels made of a linear PEG macromer copolymerized with pNIPAAm using bisacrylamide as a chemical crosslinker. The cycle-containing gels showed significantly higher swelling compared to gels containing the same amount of PEG in linear form. The authors attribute this to the movable nature of the threaded cross-links.
Photochemically Mediated Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization of Methyl Methacrylate Using ppm Amounts of Catalyst
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/ma300773t
Jaroslav Mosnacek and Marketa Ilcikova
The authors report a photochemically controlled ATRP polymerization of MMA. The polymerization is copper catalyzed, uses visible light wavelengths, and results in living polymerizations with low (~1.1) PDI.

Jaroslav Mosnacek and Marketa Ilcikova
The authors report a photochemically controlled ATRP polymerization of MMA. The polymerization is copper catalyzed, uses visible light wavelengths, and results in living polymerizations with low (~1.1) PDI.

Comparison of Arylboron-Based Nucleophiles in Ni-Catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling with Aryl Mesylates and Sulfamates
Comparison of Arylboron-Based Nucleophiles in Ni-Catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling with Aryl Mesylates and Sulfamates
Na Zhang, David J. Hoffman, Nicholas Gutsche, Jayesh Gupta, and Virgil Percec*
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jo300547v
In this paper, many factors (rate of reaction, cost of reagents, atom-economy) are compared for different arylboron-based partners for the nickel-catalyzed Suzuki Miyaura cross-coupling. The boronic acid is the most reactive of all, and the neopentylglycolboronate gives rise to more efficient cross-coupling than BPin.

Na Zhang, David J. Hoffman, Nicholas Gutsche, Jayesh Gupta, and Virgil Percec*
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jo300547v
In this paper, many factors (rate of reaction, cost of reagents, atom-economy) are compared for different arylboron-based partners for the nickel-catalyzed Suzuki Miyaura cross-coupling. The boronic acid is the most reactive of all, and the neopentylglycolboronate gives rise to more efficient cross-coupling than BPin.

Microarray with Micro- and Nano-topographies Enables Identification of the Optimal Topography for Directing the Differentiation of Primary Murine Neural Progenitor Cells
Microarray with Micro- and Nano-topographies Enables
Identification of the Optimal Topography for Directing the
Differentiation of Primary Murine Neural Progenitor Cells
Aung Aung Kywe Moe, et al.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smll.201200490/abstract
In this paper, the authors present a study of topography-dependence of murine neural progenitor cell differentiation. They find that these cells differentiate into neurons by anisotropic gratings (2 μm gratings, 250 nm gratings) and isotropic 1 μm pillars, as indicated by expression of β-III-tubulin (59%, 58%, and 58%, respectively, compared to 30% on the control). In contrast, glial differentiation is enhanced on isotropic 2 μm holes and 1 μm pillars.
Aung Aung Kywe Moe, et al.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smll.201200490/abstract
In this paper, the authors present a study of topography-dependence of murine neural progenitor cell differentiation. They find that these cells differentiate into neurons by anisotropic gratings (2 μm gratings, 250 nm gratings) and isotropic 1 μm pillars, as indicated by expression of β-III-tubulin (59%, 58%, and 58%, respectively, compared to 30% on the control). In contrast, glial differentiation is enhanced on isotropic 2 μm holes and 1 μm pillars.
N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Palladium(II)-1-Methylimidazole Complex Catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling of Aryl Sulfonates with Arylboronic Acids
N-Heterocyclic
Carbene-Palladium(II)-1-Methylimidazole Complex Catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura
Coupling of Aryl Sulfonates with Arylboronic Acids
Zhan-Yong Wang, Gao-Qi Chen, and Li-Xiong Shao
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jo301270t
In this paper, the authors show the first example of NHC-Pd(II) complex catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of aryl sulfonates including tosylates, phenylsulfonates and even the less reactive mesylates with arylboronic acids. The reaction behaves best if carried out in morpholine as solvent, and high temperatures (>100oC) are required. Still, a useful reaction, and it uses the IPr NHC.

Zhan-Yong Wang, Gao-Qi Chen, and Li-Xiong Shao
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jo301270t
In this paper, the authors show the first example of NHC-Pd(II) complex catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of aryl sulfonates including tosylates, phenylsulfonates and even the less reactive mesylates with arylboronic acids. The reaction behaves best if carried out in morpholine as solvent, and high temperatures (>100oC) are required. Still, a useful reaction, and it uses the IPr NHC.

High-Resolution Protein Structure Determination by Serial Femtosecond Crystallography
High-Resolution Protein Structure Determination by Serial Femtosecond Crystallography
Sébastien Boutet et al.
http://www.sciencemag.org/content/337/6092/362.short
In this paper, the authors report a new technique called SFX to determine crystal structure of small crystals (on the order of 0.1-10 micrometers) that are susceptible to X-ray damage. This technique relies on femtosecond pulses of x-rays, as well as on the introduction of sample as a liquid jet.
Single UV or Near IR Triggering Event Leads to Polymer Degradation into Small Molecules
Caroline de Gracia Lux, Cathryn L. McFearin, Shivanjali Joshi-Barr, Jagadis Sankaranarayanan,
Nadezda Fomina, and Adah Almutairi
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/mz3002403
From the monomers in the synthetic scheme below, polymers were made that were endcapped with either a UV degradable o-nitrobenzyl alcohol group or a NIR degradable bromo-coumarin group. Deprotection of these endgroups with the appropriate wavelength led to degradation of the polymer in a domino effect as depicted in the figure below.

Nadezda Fomina, and Adah Almutairi
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/mz3002403
From the monomers in the synthetic scheme below, polymers were made that were endcapped with either a UV degradable o-nitrobenzyl alcohol group or a NIR degradable bromo-coumarin group. Deprotection of these endgroups with the appropriate wavelength led to degradation of the polymer in a domino effect as depicted in the figure below.

Immobilization and Intracellular Delivery of an Anticancer Drug Using Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine Capsules
Biomacromolecules
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/suppl/10.1021/bm300835r
A facile approach to immobilize pH-cleavable polymer-drug conjugates in mussel-inspired polydopamine (PDA) capsules for intracellular drug delivery is reported in this paper. The anticancer drug doxorubicin (Dox) was conjugated to thiolated poly(methacrylic acid) (PMASH) with a pHcleavable hydrazone bond, and then immobilized in PDA capsules via robust thiol-catechol reactions between the polymer-drug conjugate and capsule walls. The loaded Dox showed limited release at physiological pH but significant release (over 85%) at endosomal/lysosomal pH. Cell viability assays showed that Dox-loaded PDA capsules enhanced the efficacy of eradicating HeLa cancer cells compared with free drug under the same assay conditions.

http://pubs.acs.org/doi/suppl/10.1021/bm300835r
A facile approach to immobilize pH-cleavable polymer-drug conjugates in mussel-inspired polydopamine (PDA) capsules for intracellular drug delivery is reported in this paper. The anticancer drug doxorubicin (Dox) was conjugated to thiolated poly(methacrylic acid) (PMASH) with a pHcleavable hydrazone bond, and then immobilized in PDA capsules via robust thiol-catechol reactions between the polymer-drug conjugate and capsule walls. The loaded Dox showed limited release at physiological pH but significant release (over 85%) at endosomal/lysosomal pH. Cell viability assays showed that Dox-loaded PDA capsules enhanced the efficacy of eradicating HeLa cancer cells compared with free drug under the same assay conditions.

Core–Shell Nanogels by RAFT Crosslinking Polymerization: Synthesis and Characterization
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry
A synthetic methodology is described for the preparation of core–shell
nanogels by reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer.
Well-defined macro chain transfer agents (macro-CTA's) were prepared in a
first step using monomers that yield sensitive polymers. In the second
step, a crosslinker alone or with the addition of a functionalized
comonomer were used to form a crosslinked core. The ratio of crosslinker
to macro-CTA is crucial to yield nanogels.
Self-Assembly of Inorganic Nanoparticle Vesicles and Tubules Driven by Tethered Linear Block Copolymers
Jie He, Yijing Liu, Taarika Babu, Zengjiang Wei, and Zhihong Nie Journal of the American Chemical Society 2012 134 (28), 11342-11345
This article investigates the self assembly of gold nanoparticles that
are coated with amphiphillic block copolymers (PS-PEO). These
amphiphillic colloidal molecules (ACMs) self assemble into well defined
vesciles and tubules when rehydrated in water depending on the relative
size of the gold nanoparticles and the size of the PS block. The authors
found that when R0/dAu < 0.5, vesicle formation was favorable whereas when R0/dAu = 0.5, tubules were favored. When R0/dAu > 0.5, the AMCs precipitated and could not be rehydrated.

New ladder-type conjugated polymer with broad absorption, high thermal stability, and low band gap
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry
A ladder-type π-conjugated polymer PPBBTZ was synthesized through a simple method. PPBBTZ
showed good solubility in organic solvents and high thermal
stability (decomposition temperatures up to 323 °C and 299 °C in
nitrogen and air, respectively). HOMO and LUMO are −5.46 and −3.81 eV,
respectively, with a band gap of 1.65 eV. More interestingly, PPBBTZ displayed broad absorption from ultraviolet to visible light regions (200–750 nm).
Sunday, July 15, 2012
E-selectin liposomal and nanotube-targeted delivery of doxorubicin to circulating tumor cells
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365912001435
Michael J. Mitchell, Christina S. Chen, Varun Ponmudi, Andrew D. Hughes, and Michael R. King
Liposomal doxorubicin with PEG and E-selectin coupled to the surface were used to study the possibility of targetting circulating tumor cells in the bloodstream. The E-selectin (selectins are naturally found on imflamed endothelial cells) was able to adhere to sialylated carbohydrate ligands that are often overexpressed on circulating tumor cells. The researchers were able to show that their nanoparticles immobilized along microtubules or in a cone-and-plate viscometer were able to target and kill cancer cells under shear flow, but not red blood cells.

Michael J. Mitchell, Christina S. Chen, Varun Ponmudi, Andrew D. Hughes, and Michael R. King
Liposomal doxorubicin with PEG and E-selectin coupled to the surface were used to study the possibility of targetting circulating tumor cells in the bloodstream. The E-selectin (selectins are naturally found on imflamed endothelial cells) was able to adhere to sialylated carbohydrate ligands that are often overexpressed on circulating tumor cells. The researchers were able to show that their nanoparticles immobilized along microtubules or in a cone-and-plate viscometer were able to target and kill cancer cells under shear flow, but not red blood cells.

In vivo temperature controlled ultrasound-mediated intracellular delivery of cell-impermeable compounds
Anna Yudina, Matthieu Lepetit-Coiffé, Mariska De Smet, Sander Langereis,
Holger Grüll, Chrit Moonen
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365912002593
Thermosensitive liposomes made from 1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC), 1-stearoyl-
2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (MSPC) and 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[methoxy(polyethylene glycol)-2000] (DSPE-PEG2000) were use to encapsulate TO-PRO-3, a cell-impermeable molecule that binds to nucleic acid and increases its fluorescence. Ultrasound treatment using microbubbles was used to help promote internalization of these nanoparticles, and heating to 47C helped to release the fluorophore in mice, as observed by fluorescence imaging.

Holger Grüll, Chrit Moonen
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365912002593
Thermosensitive liposomes made from 1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC), 1-stearoyl-
2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (MSPC) and 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[methoxy(polyethylene glycol)-2000] (DSPE-PEG2000) were use to encapsulate TO-PRO-3, a cell-impermeable molecule that binds to nucleic acid and increases its fluorescence. Ultrasound treatment using microbubbles was used to help promote internalization of these nanoparticles, and heating to 47C helped to release the fluorophore in mice, as observed by fluorescence imaging.

New Synthetic Routes to Z-Shape Functionalized Perylenes
Org. Lett.
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ol3014667
This new synthetic route is useful for making polyaromatic compounds.
Z-shape (1,2,7,8-tetrasubstituted) perylene derivatives are novel chromophores with great potential in various applications. In this communication, the synthesis of a series of Z-shape perylene derivatives via a double Wittig–Knoevenagel benzannulation protocol is reported. Preliminary photophysical and electrochemical studies indicate that the frontier orbital energy levels of these new perylene systems are modulated by electronic, regiochemical, and conformational effects.

http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ol3014667
This new synthetic route is useful for making polyaromatic compounds.
Z-shape (1,2,7,8-tetrasubstituted) perylene derivatives are novel chromophores with great potential in various applications. In this communication, the synthesis of a series of Z-shape perylene derivatives via a double Wittig–Knoevenagel benzannulation protocol is reported. Preliminary photophysical and electrochemical studies indicate that the frontier orbital energy levels of these new perylene systems are modulated by electronic, regiochemical, and conformational effects.

Co-delivery of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Growth Factor-Loaded Microspheres in RGD-Grafted N-Methacrylate Glycol Chitosan Gels for Focal Chondral Repair
Biomacromolecules
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bm300733n
The coencapsulation of growth factor-loaded microspheres with adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) within a hydrogel matrix was studied as a potential means to enhance ASC chondrogenesis in the development of a cell-based therapeutic strategy for the regeneration of partial thickness chondral defects. A photopolymerizable N-methacrylate glycol chitosan (MGC) was employed to form an in situ gel used to encapsulate microspheres loaded with bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP-6) and transforming growth factor-β3 (TGF-β3) with human ASCs. ASC viability and retention were enhanced when the Young’s modulus of the MGC ranged between 225 and 380 kPa. Grafting an RGD-containing peptide onto the MGC backbone (RGD-MGC) improved ASC viability within the gels. The effects of BMP-6 and TGF-β3 released from the polymer microspheres on ASC chondrogenesis were also assessed.

http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bm300733n
The coencapsulation of growth factor-loaded microspheres with adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) within a hydrogel matrix was studied as a potential means to enhance ASC chondrogenesis in the development of a cell-based therapeutic strategy for the regeneration of partial thickness chondral defects. A photopolymerizable N-methacrylate glycol chitosan (MGC) was employed to form an in situ gel used to encapsulate microspheres loaded with bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP-6) and transforming growth factor-β3 (TGF-β3) with human ASCs. ASC viability and retention were enhanced when the Young’s modulus of the MGC ranged between 225 and 380 kPa. Grafting an RGD-containing peptide onto the MGC backbone (RGD-MGC) improved ASC viability within the gels. The effects of BMP-6 and TGF-β3 released from the polymer microspheres on ASC chondrogenesis were also assessed.

Synthesis of mikto-topology star polymer containing one cyclic arm
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/pola.26226/abstract
Well-defined mikto-topology star polystyrene composed of one cyclic arm and four linear arms was synthesized by a combination of atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) and Cu-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) click reaction.
First, the bromine-alkyne α,ω-linear polystyrenes containing four hydroxyl groups protected with acetone-based ketal groups were synthesized by ATRP of styrene using a designed initiator.
Then, the bromine end-group was converted to the azide and the linear polystyrene was cyclized intra-molecularly by the CuAAC reaction.
The four hydroxyl groups were released by deprotection and then esterified with 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide to produce a cyclic polymer bearing four ATRP initiating units.
By subsequent ATRP of styrene to grow linear polymers with the cyclic polystyrene as a macroinitiator, the mikto-topology star polymers were prepared.
Controlling Thermochromism in a Photonic Block Copolymer Gel
Controlling Thermochromism in a Photonic Block Copolymer Gel
Joseph J. Walish, Yin Fan, Andrea Centrone, Edwin L. Thomas*
This
report presents a way to modulated the reflective properties of a gel.
In this case, a PS-P2VP block-copolymer in a lamellar microstructure is
a gel that can swell in only one direction b/c of the constraint
imposed by the glassy PS domain. The swelling is achieved by reversible
temperature-induced pKa change of the pyridinium moiety (decreases with
temperature). Increase in P2VP domain thickness causes specific light
frequencies to interfere constructively when reflected from the sample,
and these frequencies are dependent on the thickness of the repeating
domains.
Molecular Engineered Super-Nanodevices: Smart and Safe Delivery of Potent Drugs into Tumors
Advanced Materials
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201200954/abstractA super-nanodevice engineered at molecular level integrates various desired properties in a smart and coordinated way, and can “switch on” or “turn off” certain functionalities as required. Importantly, it can break through complex physiological barriers, and then precisely ferry potent toxic triptolide into tumor cells in vivo, thus significantly maximizing the therapeutic efficacy and reducing the drug toxicity.

Small Molecule–Gold Nanorod Conjugates Selectively Target and Induce Macrophage Cytotoxicity towards Breast Cancer Cells
Small Molecule–Gold Nanorod Conjugates Selectively Target and Induce Macrophage Cytotoxicity towards Breast Cancer Cells
Erik C. Dreaden, Sandra C. Mwakwari, Lauren A. Austin, Matthew J. Kieffer, Adegboyega K. Oyelere,* and Mostafa A. El-Sayed*
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smll.201200333/full
"Macrolide-functionalized gold nanorods were preferentially delivered to tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) cells and selectively induced TAM-dependent cytotoxicity towards breast cancer cells in co-culture. Because TAMs migrate freely in circulation, bypass the blood–brain barrier, and extensively accumulate/infiltrate into breast tumors, these data show that macrophage-targeting gold nanoparticles can serve as promising candidates for targeted cancer therapy."
However, the gold nanorods were not effective for photothermal ablation of TAMs or of the tumor cells.

Palladium-Catalyzed Borylation of Primary Alkyl Bromides
Palladium-Catalyzed Borylation of Primary Alkyl Bromides
Amruta Joshi-Pangu, Xinghua Ma, Mohamed Diane, Sidra Iqbal, Robert J Kribs, Richard Huang, Chao-Yuan Wang, and Mark R. Biscoe
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jo301156e
In this work, the authors present a mild method to generated alkyl boronic ester.
Amruta Joshi-Pangu, Xinghua Ma, Mohamed Diane, Sidra Iqbal, Robert J Kribs, Richard Huang, Chao-Yuan Wang, and Mark R. Biscoe
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jo301156e
In this work, the authors present a mild method to generated alkyl boronic ester.
Macroscopic Volume Change of Dynamic Hydrogels Induced by Reversible DNA Hybridization
Lu Peng, Mingxu You, Quan Yuan, Cuichen Wu, Da Han, Yan Chen, Zhihua Zhong, Jiangeng Xue, and Weihong Tan Journal of the American Chemical Society Article ASAP
This paper outlines the development of DNA-acrylamide hybrid hydrogels
that convert light energy to volume changes. The hydrogels are
synthesized by a two step method where two separate strands of
acrylamide that have been copolymerized with complementary DNA strands
are permanently cross-linked using methylenebisacrylamide. The DNA
strands are modified with azobenzene duplexes that isomerize from trans
to cis when irradiated with UV light. Under visible light conditions,
the DNA strands are allowed to hybridize creating extra cross-links that
cause the hydrogel to exist in a shrunken state. When irradiated with
UV light, the cis-trans isomerization of azobenzene causes the DNA
strands to denature allowing the hydrogel to expand. Using control
experiments, the authors demonstrate that the volume changes are indeed
tied to the photo-induced isomerization (though azobenzene was shown to
slowly relax to its trans state in the dark due to thermal factors).
They also demonstrate the reversibility of the volume changes over many
cycles of visible and UV light irradiation. Studies on how the
concentration of various elements effect swelling were also carried out
with the results that more permanent cross-links created for less change
overall while more DNA strands made for a more shrunken initial state.
Aromatic Cations from Oxidative Carbon–Hydrogen Bond Cleavage in Bimolecular Carbon–Carbon Bond Forming Reactions
Aromatic Cations from Oxidative Carbon–Hydrogen
Bond Cleavage in Bimolecular Carbon–Carbon Bond
Forming Reactions
Dane J. Clausen and Paul E. Floreancig*
This paper demonstrates the oxidative coupling of mild nucleophiles (e.g. allylsilane) and chromene/isochromene, where the oxidation is mediated by DDQ. The reaction goes through an oxocarbenium intermediate.
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jo301185h
Bond Cleavage in Bimolecular Carbon–Carbon Bond
Forming Reactions
Dane J. Clausen and Paul E. Floreancig*
This paper demonstrates the oxidative coupling of mild nucleophiles (e.g. allylsilane) and chromene/isochromene, where the oxidation is mediated by DDQ. The reaction goes through an oxocarbenium intermediate.
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jo301185h
The direct reductive amination of electron-deficient amine with aldehydes: the unique reactivity of the Re2O7 catalyst
Chemical Communications
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2012/CC/C2CC33185C?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+rss%2FCC+%28RSC+-+Chem.+Commun.+latest+articles%29&utm_content=Google+Reader
The authors here describe a direct reductive amination procedure using a oxo-rhenium catalyst and silanes as the hydride source. They were able to produce amines at room temperature using 3% catalyst loading without getting over alkylation.
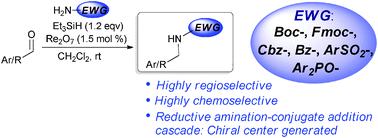
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2012/CC/C2CC33185C?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+rss%2FCC+%28RSC+-+Chem.+Commun.+latest+articles%29&utm_content=Google+Reader
The authors here describe a direct reductive amination procedure using a oxo-rhenium catalyst and silanes as the hydride source. They were able to produce amines at room temperature using 3% catalyst loading without getting over alkylation.

Sunday, July 8, 2012
Iron-Catalyzed Alkylations of Aryl Sulfamates and Carbamates
Org. Lett.
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ol301681z
The alkylation of aryl sulfamates and carbamates using iron catalysis is reported. The method constructs sp2–sp3 carbon–carbon bonds and provides synthetically useful yields across a range of substrates . The directing group ability of sulfamates and carbamates, accompanied by their low reactivity toward conventional cross-couplings, renders these substrates useful for the synthesis of polyfunctionalized arenes.

http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ol301681z
The alkylation of aryl sulfamates and carbamates using iron catalysis is reported. The method constructs sp2–sp3 carbon–carbon bonds and provides synthetically useful yields across a range of substrates . The directing group ability of sulfamates and carbamates, accompanied by their low reactivity toward conventional cross-couplings, renders these substrates useful for the synthesis of polyfunctionalized arenes.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)



